Python for IoT Development: Secure and Scalable Solutions Guide

Quick Reference
- Target Audience: Intermediate Python developers
- Python Version: 3.x
- Hardware Required: Raspberry Pi or similar IoT device
- Time to Complete: 2–3 hours
Prerequisites
- Basic Python programming knowledge
- Understanding of basic electronics
- Access to IoT hardware (Raspberry Pi recommended)
- Basic understanding of networking concepts
Introduction
With the rise of smart devices, IoT (Internet of Things) has become a major area of innovation. Python, known for its simplicity and extensive libraries, is a top choice for IoT development. This guide equips you to build scalable, secure, and efficient IoT solutions using Python.
Core Concepts of IoT Development with Python
1. Environment Setup
Ensure your development environment is properly configured before starting.
Development Environment Checklist

def verify_environment():
import sys
import pkg_resources
required_packages = {
'paho-mqtt': '1.6.1',
'RPi.GPIO': '0.7.0',
'pyserial': '3.5'
}
status = {
'python_version': sys.version,
'packages': {},
'environment_ready': True
}
for package, version in required_packages.items():
try:
dist = pkg_resources.get_distribution(package)
status['packages'][package] = {
'installed': True,
'version': dist.version,
'compatible': pkg_resources.parse_version(dist.version) >=
pkg_resources.parse_version(version)
}
except pkg_resources.DistributionNotFound:
status['packages'][package] = {'installed': False, 'compatible': False}
status['environment_ready'] = False
return status
2. Device Communication
Secure MQTT communication using SSL/TLS:
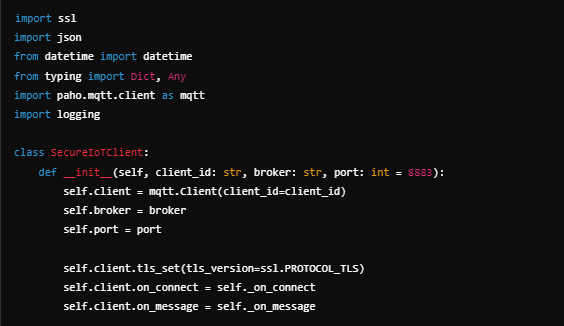
import ssl, json, logging
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, Any
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
class SecureIoTClient:
def __init__(self, client_id: str, broker: str, port: int = 8883):
self.client = mqtt.Client(client_id=client_id)
self.client.tls_set(tls_version=ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS)
self.client.on_connect = self._on_connect
self.client.on_message = self._on_message
self.broker = broker
self.port = port
def _on_connect(self, client, userdata, flags, rc):
if rc == 0:
logging.info("Connected successfully")
else:
logging.error(f"Failed to connect: {rc}")
def publish_telemetry(self, topic: str, data: Dict[str, Any]):
payload = {
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
"data": data
}
result = self.client.publish(topic, json.dumps(payload), qos=1)
return result.rc == mqtt.MQTT_ERR_SUCCESS
3. Sensor Integration
Integrate sensors using an abstract class approach.

from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import Dict, Any
class IoTSensor(ABC):
def __init__(self, pin: int):
self.pin = pin
@abstractmethod
def read(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
pass
class TemperatureSensor(IoTSensor):
def read(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {"temperature": 23.5, "humidity": 60}
Best Practices
1. Error Handling and Logging
Use retries and structured logging for robustness.

import logging
from time import sleep
from functools import wraps
def retry_with_backoff(retries: int = 3):
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
for i in range(retries):
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
sleep(2 ** i)
logging.error(f"Retry {i+1}: {e}")
return wrapper
return decorator
2. Security Implementation
Encrypt data during transmission for security.
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
class SecurityManager:
def __init__(self):
self.key = Fernet.generate_key()
self.cipher_suite = Fernet(self.key)
def encrypt_payload(self, data: str) -> bytes:
return self.cipher_suite.encrypt(data.encode())
def decrypt_payload(self, encrypted_data: bytes) -> str:
return self.cipher_suite.decrypt(encrypted_data).decode()
Project Structure

iot_project/
├── config/
│ └── settings.py
├── src/
│ ├── sensors/
│ └── communication/
├── tests/
│ └── test_mqtt.py
├── requirements.txt
└── README.md
Testing and Validation
Unit Testing Example




Comments
Post a Comment